Contents
What is a Firewall?
A computer Network Firewall is either: (1) a software program installed on your PC (2) a built-in firewall inside your modem or (3) a dedicated hardware firewall. Firewalls generally block all traffic (data transfer) unless a specific rule/exception is added to allow traffic to pass. Larger corporate networks generally use a dedicated hardware firewall.
Try to think of a firewall like a moat around your computer, and an exception rule like a bridge over the moat. The only way data can pass to and from your computer is if you add an exception rule, or a “bridge over the moat”. This exception rule can have very specific rules, or quite relaxed rules, depending on your needs. You can make exception rules for any program running on your computer, any single port ranging from 1 to 65535, or a port range like 6881 to 6889. Most users simply add an exception rule for a specific program and let that program decide which ports it needs using UPnP.
Firewall Rules Diagram
Some examples below detail the different types and complexities of exception rules.
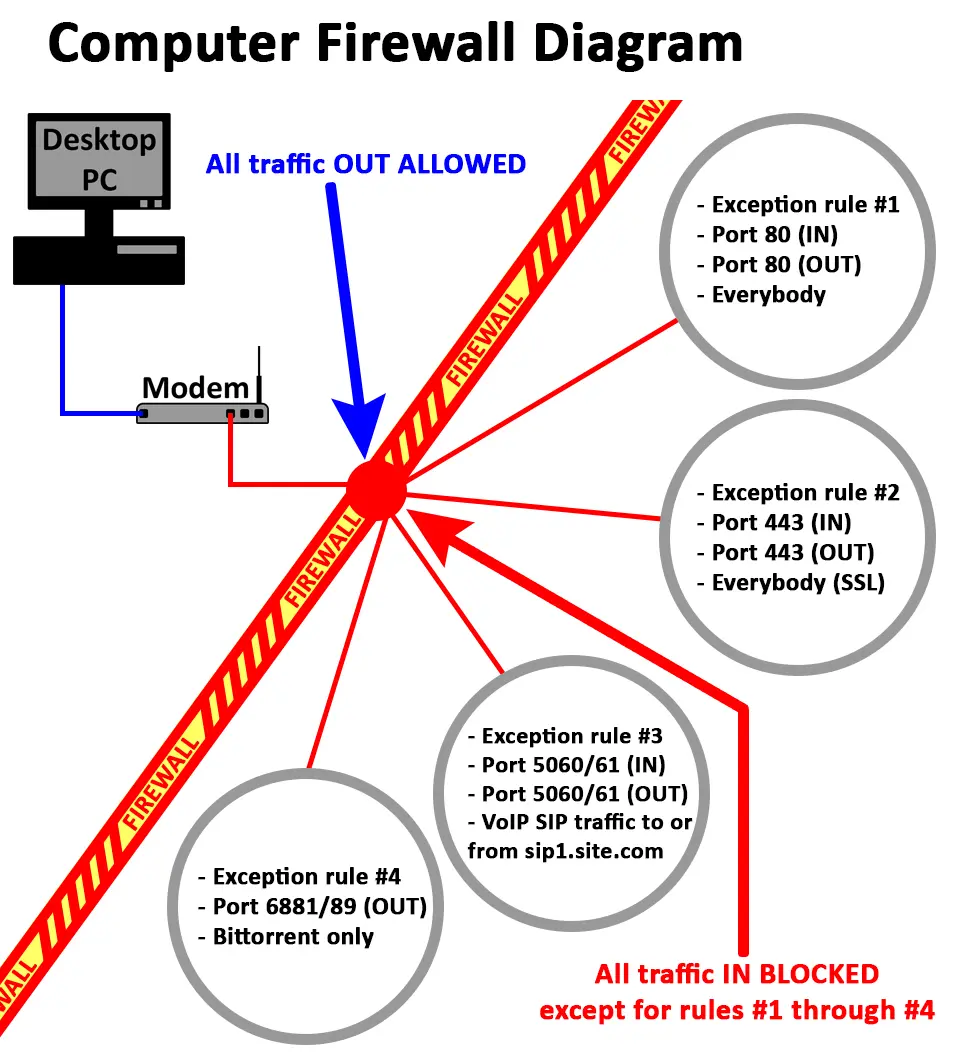
In the above diagram, the red firewall (the moat) blocks all traffic traveling IN to the private network and it’s computers by default, unless it uses one of the four exception rules (bridges over the moat). All traffic traveling OUT of the private network and to the Internet is allowed by default.
Lets go through each rule in a little more detail…
- Exception rule #1 allows all traffic on port 80 (incoming/outgoing) for everybody. This means that any computer or program attempting to send or receive data on port 80 is allowed to do so. Port 80 is widely used for almost all internet browsing traffic, such as: this page you are viewing now was sent using port 80.
- Exception rule #2 allows all traffic communicating on port 443 (incoming/outgoing) using either SSL (Secure Sockets Layer) or TLS (Transport Layer Security). Port 443, SSL and TLS are used for secure (encrypted) browsing, such as: when you log-on to your banking website.
- Exception rule #3 allows traffic communicating on port 5060 and 5061 (incoming/outgoing) but only to, or from the web address: www.sip1.site.com. Port 5060 and 5061 are used for VoIP (Voice Over Internet Protocol) traffic using SIP (Session Initiation Protocol). SIP may also need more ports, or a port range to work properly.
- Exception rule #4 allows traffic on the port range 6881 through to 6889 (outgoing) but only for the program BitTorrent which will then handle any requests from other computers on the Internet over that port range. BitTorrent is a file sharing program that may need several connections to work properly, therefore multiple ports (port range) are specified in this rule. BitTorrent would also need an extra port to listen for incoming connections but today BitTorrent programs will automatically open ports on your router using UPnP.
TCP & UDP
Although some firewalls allow you to specify TCP or UDP protocols on your port exception rules, for most users it is not necessary to specify these due to the difficulty in knowing which ports require TCP, UDP, or both.
As an example: BitTorrent does not use the UDP protocol, only TCP, and VoIP (SIP) traffic can use TCP or UDP protocols depending on the ATA device and your VoIP provider. If your firewall requires you to make a choice between TCP and UDP for your port exception rules, you can safely allow both UDP/TCP traffic without opening too big a hole in your firewall unless it is a port ranging between 1 and 1023, this port range is reserved mainly for operating system use and it is not recommended to alter any ports in this range.
Please follow the instructions of your device, service provider or installed program.


Comments
There are currently no comments on this article.
Comment